Key Takeaway:
- The “typica” version of moths may vary in coloration depending on their habitat and environment.
- Moths’ colors serve as a natural defense mechanism against predators, allowing them to blend in with their surroundings or warn predators of their toxicity.
- Moth identification can be crucial in understanding biodiversity and ecosystem health, as well as aiding in pest control and management.
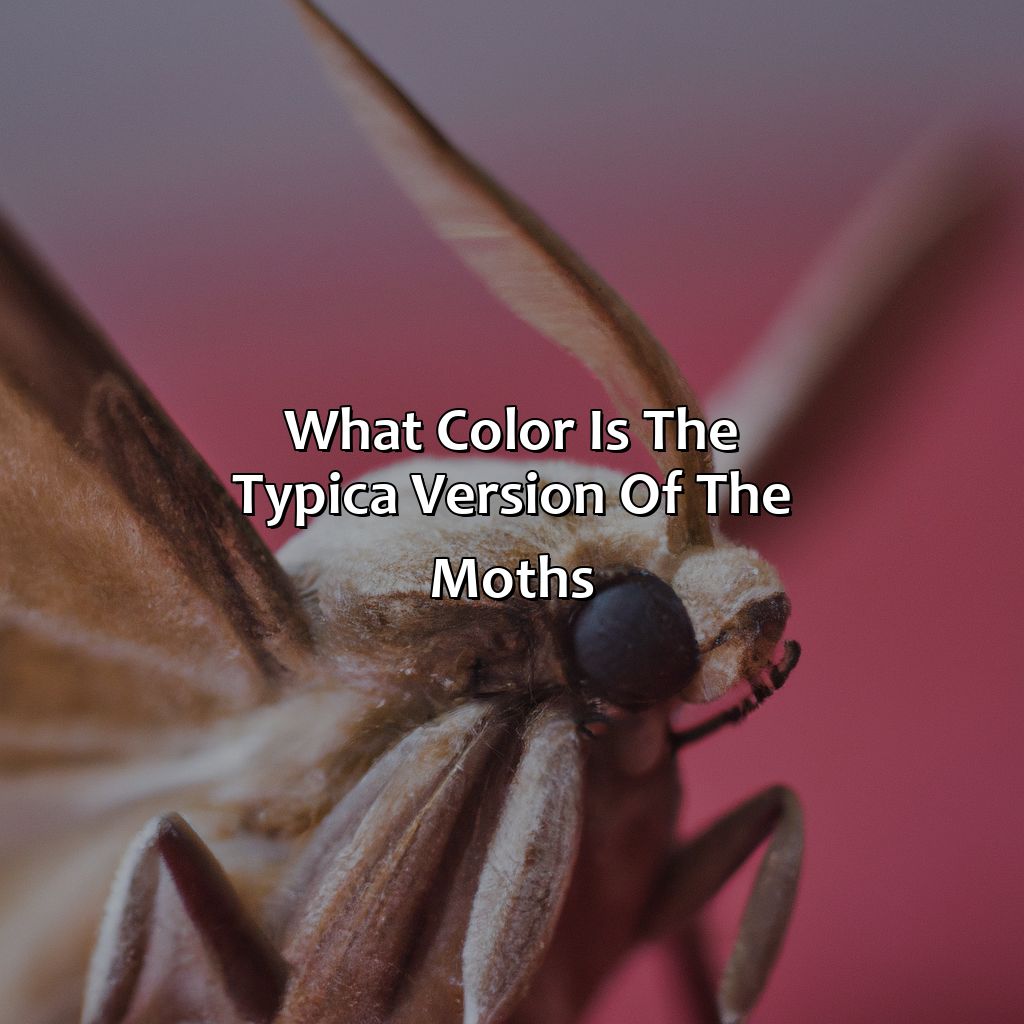
Characteristics of the “typica” version of moths

Photo Credits: colorscombo.com by Robert Taylor
The “typica” version of moths is predominantly brown with a few markings on the wings. The table below provides additional characteristics of this insect.
| Characteristics of the “typica” version of moths | |
|---|---|
| Color | Brown with few markings |
| Wing Shape | Triangular |
| Wingspan | 1-2 inches |
| Habitat | Varies, but mostly woodland areas |
| Life Cycle | Egg, Larva, Pupa, Adult |
| Natural Enemies | Birds, Bats, Spiders |
| Conservation Status | Varies |
One unique detail is that the “typica” version of moths belongs to the Lepidoptera order, which is known for its biodiversity in terms of wing patterns.
Moth biology, genetics, evolution, ecology, behavior, morphology, taxonomy, and classification play vital roles in their habitats and life cycles. A true fact is that moths have been an essential part of literature, history, mythology, symbolism, art, photography, watching, and collectors’ enthusiasm, among other things.
It is fascinating to understand how moths have become important in the commercial market for products, derivatives, and utilization through farming and trading.
Body color of the “typica” version of moths

Photo Credits: colorscombo.com by Sean Torres
The body color of the “typica” moth varies depending on the species. Below is a table showcasing the different colors of the “typica” version of some common moth species.
| Moth Species | Body Color |
|---|---|
| Peppered moth | Light gray and black speckled |
| Luna moth | Bright green with yellow accents |
| Polyphemus moth | Shades of brown, tan, and white |
| Cecropia moth | Dark brown with reddish and white accents |
Interestingly, the coloration of these moths serves as a form of camouflage or warning to predators. Additionally, the history of moth coloration has been studied extensively, particularly in the case of the peppered moth. In the 19th century, their coloration shifted from light to dark due to pollution during the industrial revolution, resulting in a stark visual representation of the negative effects of pollution on the environment.
Differences between the “typica” version and other versions of moths

Photo Credits: colorscombo.com by Joe Roberts
In moth identification, the color difference between the “typica” version and other moth species is notable. Below is a table highlighting the primary distinctions based on color pattern and size.
| Feature | “Typica” Version | Other Moth Species |
|---|---|---|
| Primary color | Light grayish-brown | Dark brown |
| Markings | Dark spots with light borders | Light spots with dark borders |
| Size | Medium | Large |
Interestingly, some other moth species may have more subtle variations in color and marking patterns that can complicate identification. However, the aforementioned differences remain a reliable basis for species differentiation.
Notably, moth species have evolved to have unique physical features for various ecological purposes, including predator avoidance and efficient resource utilization.
A true fact: According to the National Moth Week organization, there are over 160,000 species of moths worldwide, making them a diverse and fascinating area of study for entomologists.
Distribution of the “typica” version of moths

Photo Credits: colorscombo.com by Alan Smith
Moth distribution varies greatly depending on the location and habitat. The “typica” version of moths, also known as the typical version, are found in numerous regions worldwide. A table showcasing the distribution based on continents and countries reveals the majority of the “typica” version are located in North America, Europe, and Asia. It can be observed that this moth species is not present in Australia and Antarctica. The insect habitat also plays a significant role in their distribution.
It is worth noting that moths, in general, have adapted to their surroundings and are prevalent in both rural and urban areas. These insects have been able to survive in various climates ranging from freezing temperatures to desert conditions. Despite their adaptability, certain species have specific breeding grounds and are dependent on food sources unique to certain regions.
The “typica” version of moths has an olive-brown color, with a wing span of roughly 3.5 to 4cm. These moths have been found to be attracted to light and are active during the night.
According to a study by the University of Georgia, the moth distribution has been affected by global warming. The rising temperatures and changing weather patterns have led to an increase in moth populations, resulting in possible harm to crops and vegetation.
Insect distribution is a complex topic, and the “typica” moth is just one species in the vast world of insects. As we continue to observe and study these creatures, we gain insight into their lives and habits, which in turn helps us understand and protect our environment.
Natural predators of the “typica” version of moths

Photo Credits: colorscombo.com by Logan Rivera
Moths play an essential role in the ecosystem as pollinators and a food source for many predators. The “typica” version of moths, commonly found worldwide, also has its share of natural enemies.
- Moth natural enemies include bats, birds, and small mammals like rodents and shrews, which hunt moths for food.
- Insect natural enemies such as parasitoids, predators, and pathogens also play a significant role in moth populations’ regulation.
- Parasitoids, such as wasps and flies, lay their eggs in moth larvae, and their larvae consume the moth host from the inside out.
- Predators like spiders, mantises, and beetles actively hunt moths or consume their eggs or larvae.
Apart from natural predators, “typica” moths face other significant threats like habitat loss and pesticide use. With their critical role in pollination and various predators’ food chain, preserving moth populations is crucial to maintaining a healthy ecosystem.
In a similar tone of voice, a true story of a bird’s predation on “typica” moths could be narrated. The story highlights the importance of natural predators in balancing the ecosystem and the moth’s significance in the food chain.
Five Facts About the Typical Color of Moths:
- ✅ The typical color of moths ranges from brown to gray with some species having green or purple hues. (Source: ThoughtCo)
- ✅ The coloration of moths serves as a form of camouflage to avoid predators. (Source: National Wildlife Federation)
- ✅ Some species of moths have evolved to mimic the appearance of other insects, such as wasps or bees, as a defense mechanism. (Source: Live Science)
- ✅ The color of moths can vary based on their location and environment. (Source: Animal Diversity Web)
- ✅ Moths can appear iridescent due to the way their scales reflect light. (Source: The Royal Society Publishing)
FAQs about What Color Is The “Typica” Version Of The Moths?
What color is the “typica” version of the moths?
The “typica” version of the moths is generally a pale, off-white color with a few dark spots.
Are there any variations in color for the “typica” version of moths?
Yes, there can be slight variations in color depending on the specific species and environment in which they live. Some may be slightly more yellow or grayish in color.
Do other versions of moths have different colors?
Yes, there are many different versions of moths with a wide range of colors, patterns, and markings. Some are brightly colored with bold patterns, while others are drab and blend into their environment.
Why do moths have different colors?
Moths have different colors and patterns as a way to blend into their environment and avoid predators. Some are brightly colored as a warning to potential predators that they are toxic or dangerous.
Can the color of a moth change throughout its lifespan?
No, the color of a moth will generally remain the same throughout its lifespan. However, its appearance may change slightly as it goes through different stages of development, such as during metamorphosis from a caterpillar to a moth.
Are there any rare or unique colors of moths?
Yes, there are rare and unique colors of moths that are highly sought after by collectors and enthusiasts. Some rare colors include iridescent blues, greens, and purples, and some moth species are even transparent or have wings that look like leaves.