Key Takeaway:
\n
- The color of the tube used for CBC testing is important in order to ensure accurate results. The most commonly used tubes for CBC testing are lavender top tubes (EDTA), purple top tubes (EDTA), pink top tubes (EDTA), green top tubes (Lithium Heparin or Sodium Heparin), and yellow top tubes (ACD Solution A or B).
- The Lavender top tube (EDTA) is most commonly used for CBC testing because it contains an anticoagulant that prevents blood from clotting and altering the results. The Purple top tube (EDTA), Pink top tube (EDTA), Green top tube (Lithium Heparin or Sodium Heparin), and Yellow top tube (ACD Solution A or B) are less commonly used for CBC testing but may be used in certain situations.
- The selection of the tube for CBC testing depends on various factors including the age and health status of the patient, and the type of analysis required. It is important to use the correct tube for CBC testing in order to ensure accurate results and facilitate proper diagnosis, treatment, and monitoring of health conditions.
\n
\n
Understanding CBC

Photo Credits: colorscombo.com by Harold Martinez
The Complete Blood Count (CBC) test determines various components of blood and is a fundamental lab analysis comprising red and white cell count, platelets, hemoglobin, etc. Understand CBC to learn about normal CBC levels, values, sensitivity, specificity, limitations, challenges, troubleshooting, quality control, and methods. Manual and automated CBC testing methods, interferences, errors, and innovations are crucial considerations.
For optimal results, use lavender/purple top tubes. Pro Tip: Follow the protocol for timely and precise results.
Collection of CBC Sample
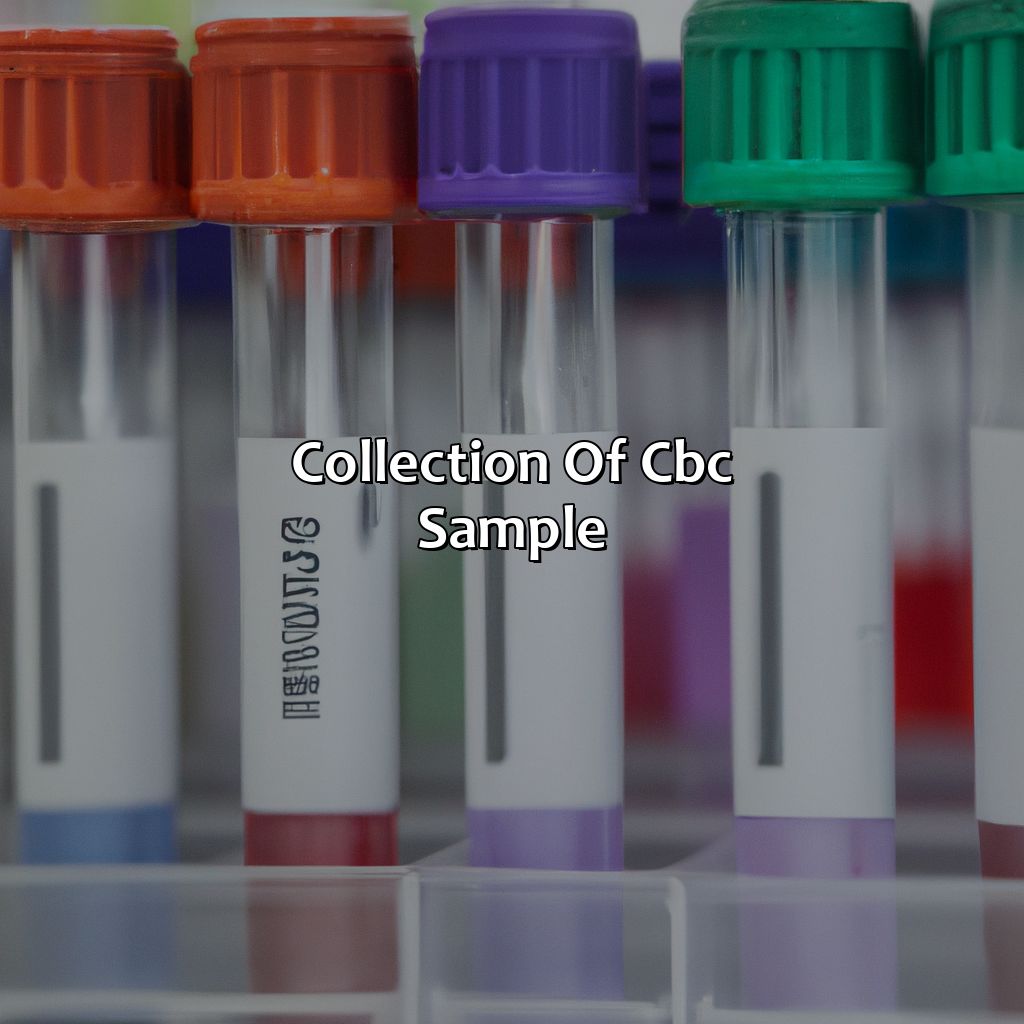
Photo Credits: colorscombo.com by Brandon Allen
Understand the need for correct tubes in a CBC sample collection. We’ll talk about the requirements, additives, and prep for the CBC collection process. Plus, discuss different CBC test types, accuracy factors, and clinical significance. Venipuncture procedure and safety precautions must be followed for accurate CBC results. Remember the value of the right blood collection tubes for CBC testing.
Venipuncture Procedure
For the accurate results of CBC, handling of the cbc test sample needs to be done with safety precautions. Here’s a guide to Venipuncture procedure that explains how to collect blood safely.
- Select a suitable arm for venipuncture, avoid using arms with limited mobility, where previous injections have been given or where lymphedema is present.
- Choose an appropriate gauge needle and check it for sharpness.
- Clean the puncture site before inserting the needle.
- Position the patient’s arm appropriately and insert the needle slowly into the vein, ensuring minimal movement of the patient’s arm during this process.
- Once blood has been drawn, remove the tourniquet before withdrawing the needle quickly.
It is essential to handle CBC test samples correctly as even slight deviations can cause significant issues during analysis.
The CBC test sample must be collected using sterile methods in order to reduce contamination rates. While obtaining larger volume samples, healthcare professionals need to pay attention to pain management techniques during drawing and effects on blood clotting time.
One patient suffered from excessive bleeding due to incorrect placement of a green top tube (Lithium Heparin or Sodium Heparin) compared with lavender top tubes (EDTA) while being diagnosed with anemia from his CVC line. Ultimately after four months company agreed for compensation claims.
Using the wrong blood collection tube for CBC is like trying to fit a square peg in a round hole – it just won’t work!
Importance of Correct Sample Collection
Correct selection of blood collection tubes for CBC is crucial in obtaining accurate results. Using the wrong tube can result in false or erroneous test results, which can lead to a wrong diagnosis and unnecessary medical interventions. It is imperative that healthcare practitioners strictly follow the tube collection protocols to ensure the consistency and reliability of test results.
The importance of using correct tubes for CBC cannot be overemphasized. The color-coded tubes are designed to collect blood samples and prevent coagulation, hemolysis, or contamination during transport. Lavender top tube (EDTA) is the most commonly used tube as it preserves cell morphology and allows for reliable WBC and platelet counts. Purple top tube (EDTA) prevents clotting by sequestering calcium ions from plasma while Pink top tube (EDTA) contains an additive that inhibits bacterial growth but may alter some leukocyte parameters.
Green top tubes (Lithium Heparin or Sodium Heparin) prevent clotting by blocking thrombin and fibrin formation while Yellow top tubes (ACD solution A or B) are used for DNA analysis of white cells or other genetic investigations. The selection of the appropriate tube depends on factors such as patient age, health status, and type of analysis required.
When it comes to CBC tube colors, it’s not just a matter of purple or lavender; it’s like a rainbow of hematology fun!
The Colors of Tubes Used for CBC

Photo Credits: colorscombo.com by Sean Martinez
Confused about cbc blood test tube colors? We can help.
Here’s a quick overview of the tubes used for CBC testing:
- Lavender top (EDTA)
- Purple Top (EDTA)
- Pink Top (EDTA)
- Green Top (Lithium Heparin or Sodium Heparin)
- Yellow Top (ACD Solution A or B)
Knowing which tube to use is key!
Lavender Top Tube
The Lavender top tube, commonly referred to as the EDTA tube, is used for collecting whole blood samples for CBC analysis. This tube contains an anticoagulant called EDTA that prevents clotting by binding calcium ions. The Lavender top tube is crucial because it inhibits platelet aggregation and preserves cell morphology during specimen storage and transportation.
During the collection of the Lavender top tube (EDTA), care must be taken to prevent hemolysis or contamination of the sample. As with other tubes, samples should be collected using a proper venipuncture procedure. After collection, the sample should be inverted gently to ensure adequate mixing with the anticoagulant.
Unlike other tubes used for CBCs, the Lavender top tube (EDTA) can accurately analyze white blood cells’ count, red cell indices, and platelet counts without damaging any cells during collection or transportation.
Pro Tip: Ensure that you choose the correct-sized needle when using a Lavender top tube, as smaller bore needles may cause hemolysis in cells due to mechanical shear forces.After all, if you’re going to collect someone’s blood, you might as well do it in style with a purple top tube (EDTA).
Purple Top Tube
The purple top tube with EDTA is commonly used for CBC (Complete Blood Count) analysis. The tube’s lavender-colored stopper indicates the presence of EDTA (ethylenediaminetetraacetic acid), an anticoagulant that binds calcium ions and inhibits clotting. It prevents blood cells from clumping together, allowing for accurate cell counts.
| Color of Tube | Additives | Uses/Tests Performed |
|---|---|---|
| Purple Top Tube | EDTA (Ethylenediaminetetraacetic Acid) |
|
It’s essential to invert the purple top tube gently after collection to ensure proper mixing of the blood with the anticoagulant. This ensures that the sample does not clot or deteriorate, which could affect the accuracy of CBC results.
To ensure accurate and reliable CBC results, healthcare professionals must select tubes according to patient age, health status, and type of analysis required.
Don’t risk inaccurate CBC results. Choose the correct tube color for your analysis – Book a consultation with a healthcare professional!
Who knew pink was more than just a color associated with Barbie dolls? It’s also the color of the tube used for EDTA collection in CBC samples.
Pink Top Tube
The Pink Top Tube (EDTA) is used for collecting blood samples to conduct CBC analysis. It contains the anticoagulant ethylenediaminetetraacetic acid (EDTA), which prevents the blood from clotting. EDTA helps in preserving cell morphology and provides accurate results for hematological parameters. The Pink Top Tube, also known as the EDTA tube, is commonly used for Hemoglobin A1c levels and hematology tests.
Additionally, EDTA binds calcium ions present in the blood, which can interfere with coagulation testing. To avoid test interference, it’s critical to vigorously invert the pink top tube at least 8-10 times immediately after collecting it.
EDTA tubes interfere with some chemical assays that require a serum or plasma sample that has not been anticoagulated by EDTA. In those cases, other types of blood collection tubes such as Serum separator tubes, Serum Red-top Tubes are used.
Fun Fact: In 1947 Karl Landsteiner and Alexander Solomon Wiener discovered an antigen called Rh factor using the pink top tube for their research.
Drawing blood is a pain, but with a green top tube, at least you won’t be feeling too blue.
Green Top Tube
Used for CBC, the green top tube (lithium heparin or sodium heparin) contains an anticoagulant which acts by preventing the blood from clotting. The tube is used in clinical laboratories to collect specimens that will be tested for common blood-related conditions.
The green top tube (lithium heparin or sodium heparin) is primarily chosen when performing certain types of tests such as liver function tests and metabolism panels. It’s also suitable for testing acid-base balance. The tube must be inverted and gently mixed at least 8 to 10 times after drawing blood so that the anticoagulant evenly distributes throughout the sample.
When selecting the appropriate collection tubes for CBC, several factors need to be considered including age and health status of the patient as well as the type of analysis required. Choosing an unsuitable tube can result in lower yields due to hemolysis or clots formation that can affect test results.
A physician was treating a patient with renal insufficiency who had a long history of hypertension and was on various medications, including lithium supplements. He ordered a green top tube (lithium heparin) for tests including electrolyte count, along with other parameters of kidney function. Unfortunately, due to incorrect handling after sample collection, hemolysis occurred causing an erroneous potassium level measurement leading to unnecessary interventions.
Why settle for just one solution when ACD gives you two?
Yellow Top Tube
The tube marked with a unique color, commonly referred to as the Yellow Top Tube (ACD Solution A or B), is used for CBC testing. ACD stands for Acid-Citrate-Dextrose, which acts as an anticoagulant and prevents blood clotting.
In the table below, you will find relevant information about the Yellow Top Tube (ACD Solution A or B) and its uses in CBC testing.
| Tube Name: | Yellow Top Tube (ACD Solution A or B) |
| Additives: | Anticoagulant: Acid-Citrate-Dextrose (ACD) Solution A or B |
| Uses: | CBC Testing, HLA phenotyping and DNA paternity testing. |
Additionally, The Yellow Top Tube (ACD Solution A or B) is usually preferred when assessing white cell DNA integrity because it preserves DNA better than the other anticoagulants used in CBC testing.
Interestingly, The development of Additive solutions such as Citrate Phosphate Dextrose Adenine (CPDA-1), Citrate Phosphate Double Dextrose (CP2D), and Citrate Phosphate Dextrose Saline-Adenine-Glucose-Mannitol Solution (CPDA-SAGM) has replaced using alternative anticoagulants such as citrates or heparin in yellow top tubes some years back.
Choosing the right tube for CBC is like selecting the perfect filter for your Instagram photo – it depends on the subject, the situation, and the desired outcome.
Tube Selection for CBC

Photo Credits: colorscombo.com by Douglas Johnson
Choosing the right tube for your CBC test is key to getting accurate and reliable results. We’ll look at tube selection for CBC and solutions for various populations. Examples include kids, elderly, expectant moms, athletes, cancer sufferers, HIV sufferers, individuals with infectious diseases, autoimmune diseases, chronic conditions, acute conditions, and genetic predispositions. Keep reading to find out more on picking the correct blood test tubes for CBC.
Age of the Patient
When it comes to selecting the correct tube for a Complete Blood Count (CBC), age of the patient is an essential factor to consider. Different age groups may require different types of tubes due to their physical development, health needs, and personal preferences.
For pediatric patients, smaller tubes with lower volume capacities like microtainer tubes are often used for CBC. These smaller tubes make it easier to collect blood samples from children without causing too much discomfort. In contrast, adult patients may require larger tubes with higher volume capacities.
Moreover, older adults may have reduced blood flow and increased fragility of blood vessels, which means that the venipuncture procedure should be carried out with extra care. For this reason, it’s important to select age-appropriate tubes that minimize any potential risk or discomfort for the patient.
Doctors know a patient’s health status better than Google does, so trust them when it comes to CBC tube selection.
Health Status of the Patient
Patients come from different backgrounds, and their health status can vary significantly. The health status of the patient refers to their overall physical and mental condition, including the presence or absence of chronic diseases, infections, or injuries. This factor can affect various blood parameters measured in CBC results. For instance, patients with chronic illnesses such as HIV/AIDS can show abnormal lymphocyte counts, while those with diabetes may have increased red blood cell indices.
Therefore, before selecting a tube for CBC analysis, it is essential to consider the patient’s health status. A physician can determine whether a patient needs an additional test or factors that may interfere with CBC results and suggest appropriate action accordingly. Clinicians should also take into account medications that patients are taking as these could affect blood parameters.
It is worth mentioning that there is no one-size-fits-all when selecting tubes for CBC tests. Different tubes have specific additives that help preserve sample integrity and prevent coagulation during testing. It is crucial to assess each patient individually considering factors like age, health status, prescribed medication, gender, and body mass index to make informed decisions about tube selection.
Research conducted by medical professionals at the Harvard Medical School suggests that age plays a critical role in determining the normal ranges for CBC test results. As individuals grow older, certain blood indices change naturally; this implies clinicians need to keep this factor in mind while assessing laboratory results (Harvard Health Publishing).
Choose your tube wisely, for the type of analysis required will determine the hue of your sample.
Type of Analysis Required
To determine the appropriate tube for CBC, it is crucial to consider the type of analysis required. The type of analysis varies from a simple complete blood count to an in-depth evaluation of the red and white blood cells using specialized techniques. Certain tubes are suitable for specific types of analysis, and choosing the correct one ensures accurate results.
The selection process of a suitable tube depends on factors such as age and health status. For instance, younger patients tend to require tubes with smaller needle gauges. Moreover, some health conditions may affect the choice of color tube. Therefore, consulting a doctor before selecting a tube for CBC is ideal.
In addition to age and health status, other factors such as turnaround time and budget considerations influence the choice of tube selection for CBC. Depending on the requested timeline and financial constraints, choosing either an expensive tube or a less costly alternative could be viable options.
To conclude, selecting the right color tube depends on various factors such as age, health status, turnaround time, and budget considerations when analyzing blood samples for CBC. Consulting with healthcare professionals will help make informed decisions while saving costs and ensuring that accuracy remains uncompromised during analysis.
Five Facts About What Color Tube for CBC:
- ✅ CBC (Complete Blood Count) test can be done using a lavender/purple top tube (EDTA) or a pink top tube (EDTA). (Source: QML Pathology)
- ✅ The lavender/purple top tube is the preferred choice for the CBC test as it contains a larger amount of anticoagulant and is able to provide more accurate results. (Source: Mayo Clinic)
- ✅ EDTA (Ethylenediaminetetraacetic acid) is a chelating agent that binds with calcium ions and prevents blood from clotting in the tube during the testing process. (Source: Healthline)
- ✅ The pink top tube (EDTA) is used for blood bank studies and for obtaining blood samples for blood typing and cross-matching. (Source: LabCorp)
- ✅ It is important to properly label the tubes before collecting the blood samples to ensure accurate test results. (Source: American Society of Hematology)
FAQs about What Color Tube For Cbc
What color tube is used for CBC?
The recommended color tube for CBC is a lavender/purple top tube which contains the anticoagulant ethylenediaminetetraacetic acid (EDTA).
Can other tubes be used for CBC?
Yes, other tubes such as pink or blue top tubes can also be used for CBC, but they may require additional steps for sample preparation and may not produce accurate results as the lavender top tube does.
Does the size of the tube matter?
Yes, the size of the tube matters as it determines the amount of blood that can be collected. A standard 2-3 mL lavender top tube is recommended for CBC.
Can a tube with a different anticoagulant be used for CBC?
No, a lavender top tube with EDTA is the recommended anticoagulant for CBC. Using a different anticoagulant may affect the accuracy of results.
What if the blood sample clots in the tube?
A clotting blood sample may yield inaccurate results for CBC. It is important to ensure proper sample collection and handling to prevent clotting. If the sample clots, it should be discarded and a new sample should be collected.
Why is CBC an important test?
CBC stands for complete blood count and it provides important information about the number and types of cells in the blood. It can help diagnose various medical conditions such as anemia, infections, and leukemia.






