Key Takeaway:
- Lavender or purple top tubes are used for hematological tests such as complete blood count (CBC) and red blood cell (RBC) analysis.
- Red top tubes are used for chemistry tests such as biochemical profile, comprehensive metabolic panel (CMP), lipid panel, electrolyte panel, liver function tests, renal function tests, thyroid function tests, hormone tests etc.
- Light blue top tubes are used for coagulation studies such as PT/INR, APTT, D-dimer, von Willebrand factor, and factor assays.
Understanding phlebotomy and blood collection

Photo Credits: colorscombo.com by Austin Wilson
Phlebotomy involves the process of vein puncture for specimen collection. This process requires a thorough understanding of the various blood collection tubes and their corresponding tests. It is important to note which color tubes are used for specific tests to avoid errors in diagnosis. By understanding these color codes and their corresponding tests, patients can be diagnosed accurately and efficiently.
Knowing which color tubes to use for different tests is essential for accurate diagnosis. A vast array of color-coded tubes are used in phlebotomy, each designed to collect a specific type of specimen. Understanding these color codes can ensure the correct tests are conducted, potentially avoiding the need for additional testing.
In addition to color-coded tubes, other factors also contribute to successful vein puncture and sample collection. Proper technique and appropriate timing also play a critical role in collecting accurate and reliable test results. It is vital that healthcare professionals receive comprehensive training in phlebotomy to ensure optimal outcomes for patients.
By staying up-to-date with the latest advancements in blood collection technology and technique, healthcare professionals can provide a safe and effective service to their patients. Don’t risk missing out on essential diagnostic information due to an error in sample collection. Ensure proper training and education in phlebotomy for optimal results every time.
Common blood tests and their requirements
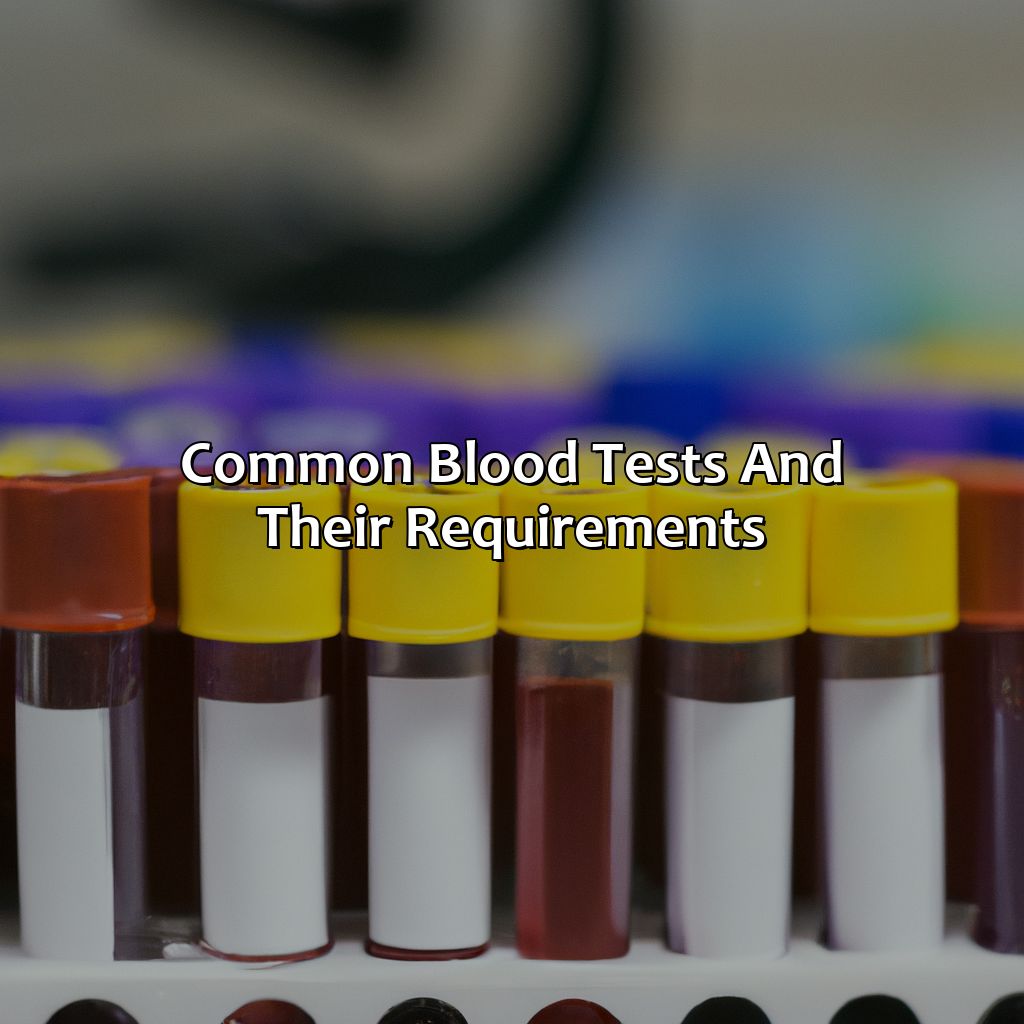
Photo Credits: colorscombo.com by Harold Hall
To comprehend the needs for common lab blood tests, take a look at “Common Blood Tests and Their Requirements.” This consists of several sub-sections. These are:
- Complete Blood Count (CBC) & Red Blood Cell (RBC) Analysis
- Biochemical Profile & Comprehensive Metabolic Panel (CMP)
- Coagulation Studies & Blood Culture
- Immunology & Serology Studies
Each sub-section explains the requirements for its respective blood test.
Complete Blood Count and Red Blood Cell Analysis
Blood count and analysis are necessary components of proper health diagnosis. The evaluation of red blood cells (RBC) is vital for determining anemia, while a Complete Blood Count (CBC) considers numerous other factors: white blood cell counts, platelet counts, hemoglobin, and hematocrit. The CBC can provide critical clues to underlying infections or chronic conditions.
| Test Name | Normal Range | Units |
|---|---|---|
| RBC Count | 4.5-5.5 x 10ˆ6 ul | /microL |
| Hemoglobin | 12-15 g/dL | grams/deciliter |
| Hematocrit | 40-50% | % |
In addition to these essential tests, the CBC can also help identify problems with production or degradation of RBCs and diagnose typical anemias such as sickle-cell disease or vitamin deficiencies.
Remember, I cannot stress enough the importance of proper phlebotomy technique in obtaining accurate results for CBC tests – to collect a sample from the right patient, at the right time using appropriate measures as instructed by medical staff.
Do not ignore your annual health checkups including blood count testing using CBC profiles. Early detection saves both trauma and money as delayed diagnoses’ treatment generates substantial medical bills. Missed opportunities lead to missed lives – get tested today!
Just remember, when it comes to chemistry tests, it’s all about finding the right balance – kind of like a science experiment, but with your blood.
Biochemical Profile and Comprehensive Metabolic Panel
Biochemical profile and comprehensive metabolic panel tests, commonly known as chemistry tests or panels, analyze the body’s chemical composition for diagnostic purposes. The test screens for different levels of electrolytes, liver function tests, renal function tests, thyroid function tests, lipid panel and hormone levels in the blood.
The table below shows some of the common chemistry panels and their requirements:
| Panel Name | Analyzed Components |
|---|---|
| Basic Metabolic Panel (BMP) | Glucose, Sodium, Potassium, Chloride, Bicarbonate, Creatinine |
| Comprehensive Metabolic Panel (CMP) | BMP+ Calcium plus other electrolytes + Liver function test + Protein test |
| Lipid Panel | Total cholesterol, HDL cholesterol,Risks ratio (LDL/HDL), Triglycerides |
Unique to CMP is a liver panel that analyzes enzyme markers for liver damage and disease such as alanine transaminase (ALT), AST/SGOT, Alkaline phosphatase, Albumin, Bilirubin.
It is important to collect the right color-coded tubes for accurate results when performing any diagnostic tests. In phlebotomy practice, LAVENDER/PURPLE TOP TUBES are used for CBC and RBC analysis while RED TOP TUBES are used for Blood group typing and biochemical profiles. LIGHT BLUE-TOPPED TUBES are added with anticoagulant sodium citrate which gel during clotting studies; GREEN TOPPED TUBE measures lithium or ammonia levels while YELLOW AND GRAY TUBE TOPS are preferred for DNA testing or drug assays, respectively. ROYAL BLUE-TOPPED TUBES contain a clot activator used primarily in trace element testing.
According to MayoClinic, Renal failure occurs when kidneys fail to filter toxins from the blood properly leading to high creatinine-negative interactions originating from nephrogenous systemic fibrosis(NSF) – thus assessment renal function among other liver checkups is of paramount importance.
Blood culture may sound like a goth band, but it’s actually a critical test in detecting infections in the bloodstream.
Coagulation Studies and Blood Culture
Coagulation and Blood Culture studies are essential tests to determine bleeding disorders or infections. The blood coagulation test, also known as PT/ INR (Prothrombin Time/ International Normalized Ratio), determines how fast the blood clots. The test is suitable for surgery patients and those on blood-thinning medication. The Blood Culture test is conducted when a patient has a recurring high fever from an unknown cause, and doctors may suspect an infection.
| Test Name | Description | Sample Type |
| Prothrombin Time (PT) | Determines clotting time of blood for patients taking Warfarin | Blue Top Tube (Sodium Citrate) |
| International Normalized Ratio (INR) | Determines clotting time of blood for patients taking Warfarin | Blue Top Tube (Sodium Citrate) |
| Blood Culture | To identify bacterial infections and their antibiotic susceptibility. | Sterile Tubes, Grey Top with Anticoagulant. |
The Coagulation Tests must be performed accurately regardless of the type of product used. False results can delay treatment or cause further complications. A proper hand hygiene procedure before drawing samples is compulsory to avoid contamination in Blood Culture studies. It’s crucial to interpret both these tests accurately to provide effective treatment.
A documented case where the incorrect use of grey-top tubes led to false readings was identified by researchers at the University of Nebraska Medical Center. The article describes how using heparin in grey-top tubes for blood culture led to 24 false-positive results, leading to unnecessary antimicrobial use and prolonged hospital stays.
Get ready to have your blood tested and your immunity questioned with these serology and immunology studies.
Immunology and Serology Studies
Immunology and serology tests utilize blood serum to evaluate the presence of antibodies or antigens that may indicate an infection, autoimmune disorder or allergy. These assessments are usually performed together to confirm a diagnosis, monitor treatment effectiveness, and evaluate immunity post-vaccination.
These tests are fundamental in detecting diseases like Hepatitis B & C, HIV/AIDS, Lyme disease, and Syphilis. Immunology tests include immunoassays such as enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA) that detect the presence of antibodies or antigens in blood serum. Serology tests use agglutination to analyze the presence of antibodies against specific antigens.
It is crucial to maintain proper aseptic technique during these procedures since samples must remain free from contamination. Gloves are mandatory while collecting patient samples for these sensitive assays. Additionally, clinicians administering vaccines should review serological testing results before vaccinating against common viruses like measles, mumps & rubella.
In several countries, serological testing has been used to estimate population-level prevalence of COVID-19 as well as in contact tracing measures. These tests aimed at identifying individuals who may have developed immunity post-infection with SARS-CoV-2.
Understanding how Immunology and Serology Studies work will help build trust between patients and medical personnel when performing diagnostic bloodwork.
From lavender for anemia testing to green for toxicology, phlebotomy tubes come in a rainbow of colors – just don’t mix them up or your patient might turn into a smurf!
Colors of phlebotomy tubes for different tests

Photo Credits: colorscombo.com by Andrew Taylor
Discover the colors of phlebotomy tubes and which medical tests they are for. Each color indicates an additive or no additive.
The following sub-sections reveal the colors for:
- Hematology tests
- Coagulation tests
- Chemistry tests
- Serology tests
- Immunohematology tests
- Molecular tests
- Toxicology tests
Lavender/Purple Top Tubes
The lavender/purple top tubes are used in phlebotomy to collect blood for specific tests. These tubes contain an anticoagulant called EDTA (Ethylenediaminetetraacetic acid) which prevents the blood from clotting by binding calcium ions.
| Test Name | Tube Type | Color |
|---|---|---|
| Complete Blood Count (CBC) and Red Blood Cell (RBC) Analysis | Lavender/Purple Top Tubes | Purple |
The lavender/purple top tubes are used to collect blood for genetic testing, hematological studies, and HIV testing. They also aid in diagnosing diseases related to the immune system, such as lupus or rheumatoid arthritis.
Pro Tip: Always ensure that the lavender/purple top tube is inverted immediately after collection to mix the anticoagulant with the blood. This aids in preventing clots and ensuring accurate results.
Don’t worry, the red top tubes won’t make you see red. But they will help diagnose your blood-related issues.
Red Top Tubes
With their distinct red top, these phlebotomy tubes contain no additive, which makes them ideal for serum collection and blood bank testing. The clot activator present in the tube promotes coagulation and speedy separation of serum from the blood.
In addition to their suitability for serum collection, red top tubes are valuable in obtaining a variety of tests, including various lipid profiles and glucose levels. Unlike other tubes that require specialized additives or elements, the simplicity of a plain red top tube simplifies many diagnostic processes.
It’s essential always to label red top tubes correctly since any confusion could lead to using incorrect data or having to redraw the sample. Remember that missed samples not only lead to alarming misdiagnoses but also risky treatment delays; hence each tube should be appropriately labeled immediately after collection.
Don’t miss out on correctly identifying and labeling your red top tubes before sending them off for processing, as this can mean possible complications or poor management down the line. Incorrectly labeled tubes may be rejected by laboratories leading to expensive retesting and delaying necessary diagnoses.
Blue is not just a color, it’s a top tube for coagulation studies in phlebotomy.
Light Blue Top Tubes
Light blue top tubes are an essential tool for coagulation studies. The blue top tube contains 3.2% sodium citrate, used to stop the enzymatic activity in clotting factors. Once centrifuged, the plasma is separated from red blood cells (RBCs) and tested for prothrombin and activated partial thromboplastin time (PT and APTT). The amount of citrate in the tube is precisely measured, so no over/under-filling or wrong preservative usage should occur.
A different amount of citrate in each tube can result in clotting variations. It is important to ensure that at least 90% fill volume saturation is achieved and mixed immediately after collection to prevent the clumping of platelets. Hemolysis might cause false-positive results leading to erroneous diagnosis/treatment and erroneous rejection of specimens due to unsuitable storage conditions.
When re-collection is necessary, discard the first drawn sample since residual tissue factor might distort test results. Use a new light blue top tube if additives were present in another sample before since it could affect PT/INR values by adding K2EDTA/Tourniquets or Heparin from previously collected samples.
Pro Tip: Ensuring that preparation materials contain sufficient anticoagulant agents such as blue-top tubes will help minimize percentages of false-positive results when analyzing blood specimen samples taken from patients during testing procedures within hospitals or labs.
Green top tubes: making patients feel like they’re getting a shot of kale juice at the juice bar.
Green Top Tubes
These tubes have a unique design that helps with accurate sample collection by minimizing the possibility of hemolysis or contamination. They are recommended for use only in Venous whole blood collection.
It is worth mentioning that improper tube selection can result in inaccurate test results leading to wrong diagnosis and treatments. Therefore, it is essential always to adhere to the phlebotomy standards when using green top tubes for collecting blood samples.
According to the American Association of Blood Banks (AABB), “compliance with standard operating procedures (SOP) significantly reduces errors associated with sample mislabeling.”
Caution: When using a yellow top tube, make sure it’s for the right test or your results may turn as sour as a lemon.
Yellow Top Tubes
Yellow top tubes are used in phlebotomy for the collection of blood samples for specific tests including blood culture, DNA testing, and paternity testing. These tubes contain an additive called sodium polyanetholesulfonate (SPS) that maintains the sterility of the collected samples and prevents the growth of bacteria. The material used in yellow top tubes helps to extract plasma from the blood quickly, which is essential for accurate test results.
Additionally, the use of yellow top tubes requires careful handling and labeling to avoid contamination or misidentification of samples. The tube must be gently inverted several times after collection to ensure proper mixing with anticoagulants within. Furthermore, it is important to ensure that these labeled yellow top tubes are transported and stored at appropriate temperatures and durations.
A study conducted by The Journal of Clinical Microbiology showed that improper refrigeration can result in changes to sample pH levels and even lead to bacterial overgrowth within 24 hours. Therefore, prompt transportation and appropriate storage are crucial steps in ensuring accurate results for tests performed on yellow top tubes.
Gray tops are like that one friend who always brings up conspiracy theories at the party – they’re primarily used for specialized tests and can make things a bit uncomfortable.
Gray Top Tubes
Below is a table detailing the specifications of Gray Top Tubes:
| Type of Tube | Additive | Tests Performed |
|---|---|---|
| Gray Top Tube | Sodium Fluoride and Potassium Oxalate | Glucose testing and alcohol level tests |
Gray top tubes have slow filling capacities, making it essential to allow them more time for complete collection. Upon collection, gently invert the tube 8 to 10 times to help mix additives thoroughly.
Historically, Gray Top Tubes were first introduced in 1959 by BD (Becton Dickinson) as a means of collecting blood samples for glucose testing. Today, these tubes continue to be popular due to their unique features.
Why settle for regular blue when you can go royal? Discover the purpose and significance of using royal blue top tubes in phlebotomy.
Royal Blue Top Tubes
Royal blue top tubes are specifically used for trace element and toxicology testing. These tubes have a special coating that prevents contamination from the chemicals used for testing. The additive in the tube contains K2EDTA, which chelates metal ions, thereby ensuring accurate test results. The unique feature of these tubes is its ability to facilitate the analysis of extremely low levels of certain elements, including lead and zinc.
According to Hemoglobe, a healthcare information website, using royal blue top tubes is necessary for accurate measurement of trace element concentrations in blood samples due to their superior purity and low detection limits.
Five Facts About What Color Tubes Are Used for Which Tests in Phlebotomy:
- ✅ Light blue tubes are used for coagulation tests, such as prothrombin time (PT) and activated partial thromboplastin time (aPTT). (Source: LabCE)
- ✅ Red tubes are used for routine tests, such as complete blood count (CBC) and blood glucose tests. (Source: WebMD)
- ✅ Green tubes are used for chemistry tests, such as liver function tests (LFTs) and electrolyte tests. (Source: UnityPoint Health)
- ✅ Lavender tubes are used for hematological tests, such as complete blood count (CBC) and erythrocyte sedimentation rate (ESR). (Source: Verywell Health)
- ✅ Gray tubes are used for glucose tolerance tests (GTT) and lactate tests. (Source: Cleveland Clinic)
FAQs about What Color Tubes Are Used For Which Tests In Phlebotomy
What color tubes are used for which tests in phlebotomy?
1. Which color tube is used for a complete blood count (CBC)?
The lavender or purple tube is used for a complete blood count (CBC).
2. Which color tube is used for chemistry tests?
The green tube is primarily used for chemistry tests.
3. Which color tube is used for coagulation tests?
The light blue tube is used for coagulation tests.
4. Which color tube is used for blood glucose tests?
The gray tube is used for blood glucose tests.
5. Which color tube is used for blood culture tests?
The yellow tube is used for blood culture tests.
6. Which color tube is used for drug level monitoring?
The red tube is used for drug level monitoring.






