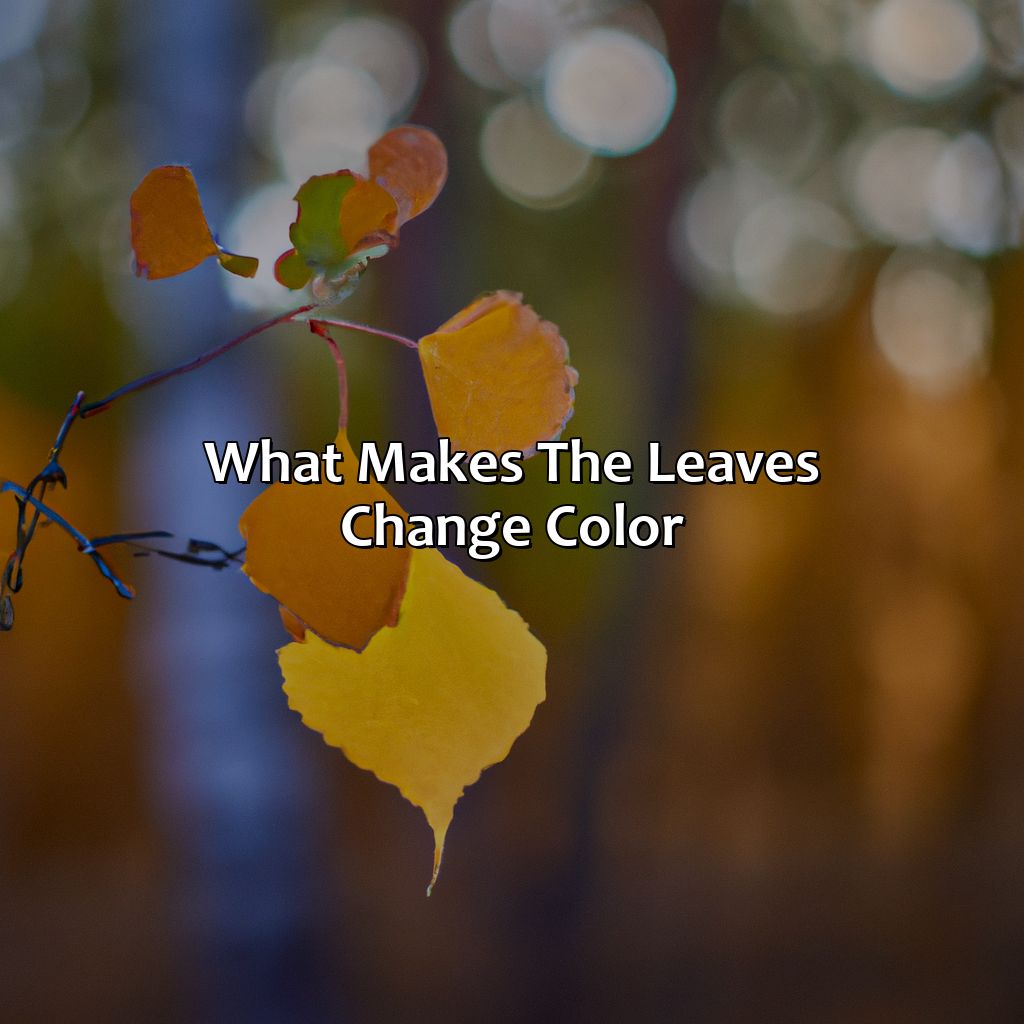Key Takeaway:
- Leaves change color in the fall due to the breakdown of chlorophyll, which reveals other pigments such as carotenoids and anthocyanins.
- Temperature, weather conditions, amount of sunlight, and day length all play a role in the color change of leaves. Tree and plant species also determine the type of pigments present and the shades of color.
- Fall is a season that triggers and enhances the leaf color change, making it a spectacular natural phenomenon to appreciate and enjoy.
The Science behind Leaves Changing Colors

Photo Credits: colorscombo.com by Noah Wilson
Grasp the science of leaves changing colors? We’ll cover it! Focusing on chlorophyll, carotenoids and anthocyanins. This section will help you fully understand leaf pigmentation. We’ll explore the roles of each pigment, and their importance in the changing of leaf colors. Sub-sections will go over chlorophyll, carotenoids, and anthocyanins.
Chlorophyll: The Green Pigment
The color green in leaves comes from the pigment chlorophyll. Chlorophyll is responsible for capturing sunlight and turning it into energy through the process of photosynthesis. It is present in large amounts during spring and summer months, giving leaves their green appearance.
In autumn, when the days become shorter and cooler temperatures arrive, trees slow down the production of chlorophyll. As a result, the green pigment breaks down and reveals other pigments that were present in lower amounts during the warmer months.
These additional pigments are called carotenoids and anthocyanins. Carotenoids are yellow-orange in color, while anthocyanins are red, purple, or blue. Their levels increase to replace chlorophyll’s decline, giving leaves their colorful autumn hues.
It is fascinating to note how different species have varying ratios of these pigments which result in different colour changes throughout fall. Furthermore, certain external factors like temperature variations and sunlight play a crucial role in influencing color changes.
A nature-loving hiker once shared his experience on how he stumbled upon a tree with leaves changing colors at uneven intervals. He found out later that this can happen due to variation in shade exposure on individual branches – an exciting observation proving that even minor environmental factors influence plant growth!
Why settle for pumpkin spice when you can have trees turning into giant piles of cheese puffs with the help of carotenoids?
Carotenoids: The Yellow-Orange Pigment
The yellow-orange pigments found in leaves are caused by carotenoids. These pigments are also present in fruits, flowers, and other parts of plants. Carotenoids act as accessory pigments to aid chlorophyll in photosynthesis but are only used when there is an abundance of light energy. During autumn, diminishing sunlight causes chlorophyll degradation leading to the display of these bright colors, especially in deciduous trees. The intensity of carotenoid production varies among plant species and can be influenced by environmental factors such as temperature and nutrient availability.
Carotenoids are a group of organic compounds that give leaves their distinctive yellow and orange hues. They absorb blue-green and violet light wavelengths while reflecting yellow, orange, or red ones. Unlike chlorophylls, carotenoids’ pigmentation doesn’t change much during the leaf’s lifecycle because they have antioxidant properties that protect photosynthetic membranes from free radicals damage caused by excessive light.
Interestingly, some research suggests that carotenoid production may be linked to a tree’s defense mechanisms against herbivores or pathogen attacks rather than simply acting as accessory pigments. For example, studies showed that ginkgo trees located near urban areas with high O3 concentrations produced more carotenoids than those growing naturally.
Records dating back centuries highlight the beauty of fall foliage displays worldwide. The composition of colorants changes subtly each year based on weather patterns like rainfall amounts and average temperatures throughout spring and summer preceding the fall foliage season. In years with cooler temperatures or bright sunny days followed by chilly nights, it’s possible to achieve an intense range of purple-reds contrasted with yellows and oranges – all thanks to nature’s complex chemical reactions!
Anthocyanins: The rebels of the leaf world, breaking all color rules with their red, purple, and blue hues.
Anthocyanins: The Red, Purple, and Blue Pigment
Plants synthesize various pigments for photosynthesis and photoprotection. Anthocyanins are water-soluble pigments with brilliant red, purple, and blue colors found in leaves, stems, flowers, and fruits. The function of anthocyanins is to attract pollinators, deter herbivores, regulate nutrient transportation, and protect against UV radiation. Anthocyanins are synthesized in cytoplasmic vesicles called vacuoles from phenylalanine or tyrosine precursors by a series of enzymes whose activity is enhanced by low pH. Some plants only produce anthocyanins under certain conditions or at specific stages of development.
Anthocyanin accumulation can be stimulated by environmental triggers such as light intensity, temperature fluctuations, nutrient availability, drought stress, and hormonal signaling. In autumn, the decreased day length and cool temperatures signal trees to discontinue chlorophyll production to conserve energy. Chlorophyll masks the colors of other pigments present in leaves like carotenoids and anthocyanins during summer. As a result of this decline in chlorophyll content when sunlight becomes less intense leaves display the vibrant colors of carotenoids (yellow-orange) and anthocyanins (red-purple-blue).
Interestingly researchers discovered that due to global warming there has been an increase in average annual temperatures which alters the phenological clock leading to delayed flowering dates hence affecting plant-pollinator interactions; for example bees adjust their foraging behavior if not attracted to flower color change.
One species of plant commonly used for extracting anthocyanins as natural colorants is red cabbage. Scientists have found it yields more yield from shade-grown cabbage due to higher levels of anthocyainns synthesized through adpatation mechanisms needed protect chlorophyll loss. This anecdote exemplifies how complex integration between different aspects of physiology mediated by chemical signaling fulfills multiple functions enabling survival strategies while producing striking visual displays in the autumn landscape.
Leaves changing color is like mood rings for trees, influenced by temperature, weather, sunlight, day length, and their species identity.
Factors that Influence the Color Change of Leaves

Photo Credits: colorscombo.com by Albert Wilson
For an insight into what causes leaves to change color, consider the temperature, weather, sunlight, day length, and species of trees/plants.
Learn how temp and weather affect leaves! Sunlight and day length are also important. And biology and hormones play a part too in the seasonal transformation of tree/plant species.
Temperature and Weather Conditions
The color change in leaves is greatly influenced by external factors, including temperature and weather conditions. Variations in temperature throughout the day can contribute to the breakdown of chlorophyll, which ultimately unveils other pigments within the leaves. Extreme weather conditions such as wind and heavy rainfall can lead to physical damage on the delicate leaf structures affecting their ability to photosynthesize appropriately.
Here are a few intrinsic details of how temperature and weather conditions impact leaf color changes:
- Temperature shifts between warm days and chilly nights trigger biochemical processes that initiate pigment production;
- Frost bites on leaves could quickly alter pigments resulting in unique patterns of color;
- Consistent dry or wet climate can either accentuate or hinder color saturation.
It’s essential to note that while all trees and plants undergo a transformative period during fall season, varying climatic conditions could determine how pronounced these changes will be for each plant species. To experience nature’s full beauty this season, plan outings when temperatures begin to shift and keep a lookout for local foliage trackers.
Don’t miss out on nature’s visual wonders by failing to take advantage of peak seasons. Plan ahead, appreciate each plant’s unique beauty and learn about autumn colors.
Leaves are like vampires, they change color depending on how much sunlight they get and how long their day is.
Amount of Sunlight and Day Length
The amount of sunlight and day length has a significant impact on the color change of leaves. Here’s how it works:
Column 1 | Column 2
———— | ————-
Sunlight | Shortening Day Length
High levels of sunlight during the growing season stimulate the production of chlorophyll, which makes leaves green. As days get shorter in fall, plants produce less chlorophyll, leading to yellow and orange pigments to appear more prominently. The shorter days cause changes in plant hormones that initiate the process for abscission or leaf dropping. This process also helps to break down the chlorophyll within leaves allowing other pigments like anthocyanins to reveal their colors more prominently.
It is interesting to note that although shorter days are one factor influencing fall colors, they are not solely responsible for this colorful display. Additionally, trees grown in urban areas with artificial lighting tend to hold onto their leaves longer and may actually end up delaying their color change.
Don’t miss out on experiencing nature’s beautiful transitions during autumn. Plan a visit to a park or a countryside area where you can witness firsthand how daylight and temperature changes influence nature’s behavior!
Deciduous trees may shed their leaves, but they still put on a colorful show thanks to plant hormones and metabolic processes that make leaf biology quite fascinating.
Trees and Plants Species
Deciduous Trees and Leaf Biology
Deciduous tree leaves vary in color as they change during autumn, influenced by the plant’s biology. The biology behind trees and plants is complex, including chemical reactions that occur within them, such as photosynthesis and metabolic processes regulated by plant hormones.
- Tree Biology: Different species of trees have unique leaf structures, sizes, shapes and textures that all play a role in determining how they change color in the fall.
- Leaf Biology: The changing colors also depend on chloroplast pigmentation (chlorophyll), carotenoids pigmentation (yellow-orange) and anthocyanins pigmentation (red-purple-blue) that are present inside each leaf.
- Plant Hormones: Another factor that influences the coloring of leaves is the presence or absence of phytohormones, such as auxins and cytokinins which affect photosynthesis efficiency.
- Metabolic Processes: Metabolic enzymes break down cell walls after exposure to sunlight which can trigger changes in color.
- Different stages in Phenology: Variations in phenology affect how deciduous trees lose their leaves during seasonal transitions.
- The intensity of Light: Sunlight plays an essential role since deciduous tree leaves’ colors change depending upon levels of light received.
Deciduous tree species have unique characteristics that lead to variations in how they change colors; for instance, some trees tend to keep their green pigments longer than others while losing reds earlier. These differences make autumn a colorful season worthy of admiration.
Interestingly, due to climate change, researchers noticed phenology shifting over time with earlier leafing emergence across various parts of the world which threaten ecosystem density leading to increased carbon dioxide concentration globally.
Autumn, where trees show off their true colors before shedding their leaves like a bad habit.
The Role of Fall in Leaves Changing Colors

Photo Credits: colorscombo.com by Richard Harris
Fall, also known as autumnal equinox, plays a significant role in the leaf color change process. As the days get shorter and temperatures drop, the solar angle decreases, causing the production of chlorophyll to slow down and revealing the pigments that give leaves their colors. Environmental triggers such as temperature and sunlight intensity affect the timing, duration and intensity of the color change.
The foliage season offers a foliage spectacle, revealing the ecological significance and natural phenomenon of tree adaptation and leaf rejuvenation. Pro Tip: To fully appreciate the natural beauty of the fall landscape, observe the leaf anatomy, leaf health and variety of leaf patterns as they undergo leaf transformation and show their fall colors.
Five Facts About Why Leaves Change Color:
- ✅ Chlorophyll breaks down in leaves during autumn, revealing other pigments that were previously masked. (Source: National Geographic)
- ✅ Carotenoids and anthocyanins are two pigments that contribute to the vibrant colors of fall foliage. (Source: USDA)
- ✅ Cooler temperatures and longer nights trigger the chemical process that leads to leaf color change. (Source: Farmer’s Almanac)
- ✅ Trees with a high sugar content in their leaves, such as maple and oak, generally display brighter fall colors. (Source: Science Daily)
- ✅ Climate change can affect the timing and intensity of fall foliage colors. (Source: The New York Times)
FAQs about What Makes The Leaves Change Color
What makes the leaves change color?
The color change in leaves is due to the breakdown of chlorophyll, which is the pigment responsible for giving leaves their green color. As a result, other pigments like carotenoids (yellow, orange) and anthocyanins (red, purple) become visible.
What triggers the breakdown of chlorophyll?
The breakdown of chlorophyll is triggered by a decrease in sunlight and cooler temperatures in the fall. This causes the tree to start preparing for winter dormancy by absorbing nutrients from the leaves and breaking down chlorophyll.
Why do leaves in different regions change color at different times?
Leaves change color at different times depending on a variety of factors, including the species of tree, climate, and altitude. Trees at higher elevations and cooler climates will change color earlier, while those in warmer climates will change later.
Do all trees change color in the fall?
No, not all trees change color in the fall. Evergreen trees retain their leaves year-round and do not go through the process of changing color and shedding leaves in the fall.
Can the intensity of fall colors vary from year to year?
Yes, the intensity of fall colors can vary from year to year depending on weather patterns. Bright, sunny days followed by cool nights are ideal for producing vibrant fall colors, while extended periods of rain or warm temperatures can dull the colors.
What is the purpose of the color change in leaves?
The color change in leaves is part of a natural process that helps trees prepare for winter dormancy and conserve energy. Once the chlorophyll breaks down and the other pigments become visible, the tree can begin to absorb nutrients from the leaves and shed them for the winter.